The greater palatine nerve block is a commonly used anesthetic technique in dentistry that provides profound anesthesia to the palatal tissues of the posterior maxilla. This article will delve into the significance, indications, technique, and potential complications of this nerve block, ensuring that dental practitioners and students alike have a solid understanding of its application.
What is the Greater Palatine Nerve Block?
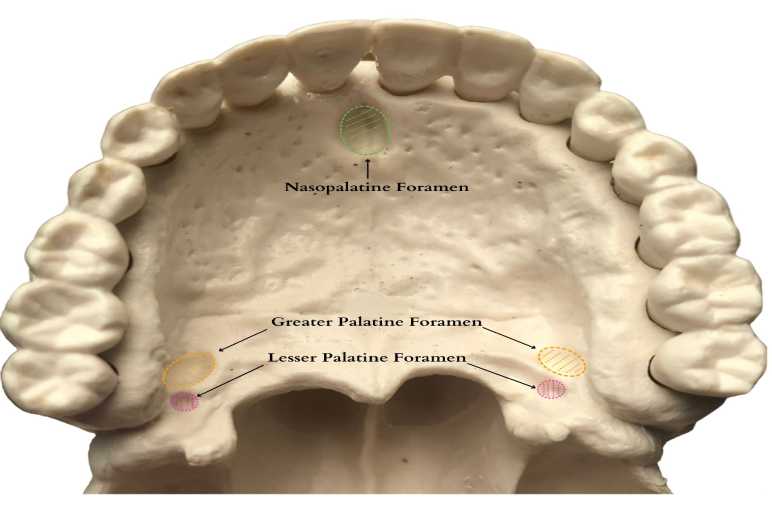
The greater palatine nerve block involves the anesthetization of the greater palatine nerve, a branch of the maxillary nerve (V2), which innervates the hard palate and the palatal mucosa. The technique is primarily employed to manage pain during dental procedures involving the posterior maxillary region, including tooth extractions, periodontal treatments, and surgical procedures.
Indications for the Greater Palatine Nerve Block
The greater palatine nerve block is indicated in various dental procedures, such as:
- Tooth Extraction: Particularly for the maxillary molars where palatal anesthesia is required.
- Periodontal Procedures: Procedures involving the palatal soft tissues.
- Surgical Procedures: Operations involving the maxilla, such as cyst or tumor removals.
- Palatal Pain Management: For patients experiencing pain in the palatal region due to various conditions.
Anatomy of the Greater Palatine Nerve
Understanding the anatomy of the greater palatine nerve is crucial for successfully administering the block. The nerve exits the greater palatine foramen, located approximately 1-2 cm anterior to the maxillary molars, and travels anteriorly along the hard palate.
The palatine arteries and other nerves, including the lesser palatine nerves, are also present in the vicinity. Knowledge of these anatomical landmarks can help in avoiding complications during the procedure.
Performing the Greater Palatine Nerve Block
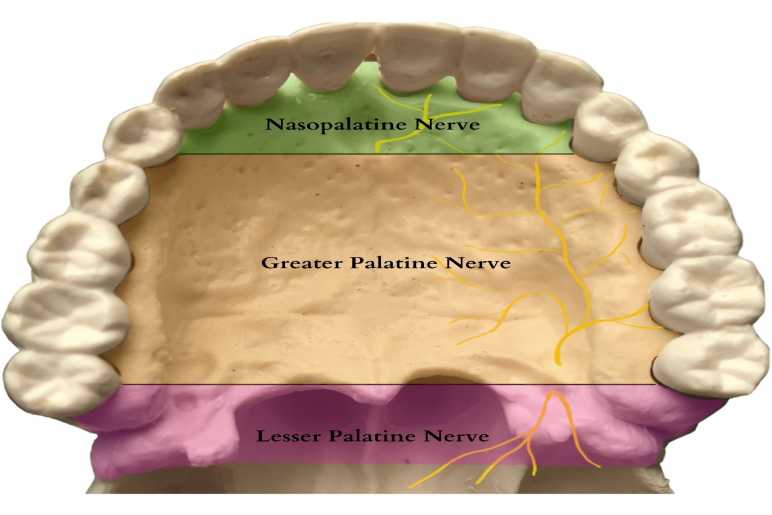
Step-by-Step Technique
- Preparation: Gather all necessary instruments, including a syringe, needle (usually a 27-gauge short needle), and local anesthetic solution. Prepare the patient by explaining the procedure to alleviate anxiety.
- Positioning: Have the patient seated comfortably in a dental chair with a clear view of the maxillary arch. The head should be slightly tilted back to expose the hard palate.
- Palpation: Using a gloved finger, locate the greater palatine foramen on the posterior part of the hard palate. This is usually found between the second and third molars.
- Needle Insertion: Insert the needle perpendicular to the palatal mucosa, about 1-2 mm anterior to the greater palatine foramen. The insertion should be gentle to avoid trauma to the tissue.
- Aspiration: Aspirate to ensure that the needle is not in a blood vessel. This step is crucial to prevent complications.
- Injection: Slowly inject approximately 0.5-1.0 mL of the anesthetic solution. If resistance is felt, withdraw the needle slightly and continue the injection.
- Observation: After the injection, wait a few minutes for the anesthetic to take effect. Test for anesthesia by checking the patient’s sensation in the targeted area.
Advantages of the Greater Palatine Nerve Block
The greater palatine nerve block offers several benefits in dental practice:
- Effective Pain Control: It provides profound anesthesia for procedures involving the hard palate, enhancing patient comfort.
- Reduced Need for Multiple Injections: By targeting the greater palatine nerve, dentists can minimize the number of injections required, improving the overall experience for patients.
- Simplicity: The technique is relatively simple and can be mastered with practice, making it a valuable addition to a dentist’s skill set.
Potential Complications
While the greater palatine nerve block is generally safe, it is essential to be aware of potential complications:
- Hemorrhage: Accidental puncture of blood vessels can lead to bleeding in the area.
- Nerve Injury: Although rare, there is a possibility of injuring surrounding nerves, leading to temporary or permanent numbness.
- Infection: As with any injection, there is a risk of infection at the injection site.
- Systemic Complications: Rarely, if anesthetic is accidentally injected into a blood vessel, systemic toxicity may occur, leading to symptoms like dizziness, tingling, or seizures.
Conclusion
The greater palatine nerve block is a vital technique in modern dentistry, providing effective pain management for various procedures. By mastering this technique, dental professionals can enhance patient experiences, reduce anxiety, and promote successful treatment outcomes.
For those looking to further their dental education or improve their clinical skills, partnering with a reliable resource like Ab Dentalogic can be instrumental. They offer comprehensive training programs and educational materials focused on essential dental techniques, including nerve blocks. Investing time in learning about the greater palatine nerve block and its applications will ultimately lead to better patient care and satisfaction.
Final Thoughts
As the field of dentistry continues to evolve, staying updated on techniques like the greater palatine nerve block is essential for practitioners aiming to provide the highest quality of care. By understanding its applications, techniques, and potential complications, dentists can ensure their patients receive optimal pain management during their dental procedures.
Embrace the importance of continued education, and consider resources like Ab Dentalogic to enhance your knowledge and skills in this critical area of dentistry. With the right training and expertise, the greater palatine nerve block can become a valuable tool in your clinical practice.
Have A Look :-
