Maxillary molar access opening is a crucial procedure in endodontic treatment. When performed correctly, it allows for efficient root canal therapy, ensuring that the infected pulp is removed while preserving the integrity of the tooth structure. This blog explores the importance of maxillary molar access opening, the step-by-step process involved, and some helpful tips for dental professionals to master this technique.
Understanding Maxillary Molar Anatomy
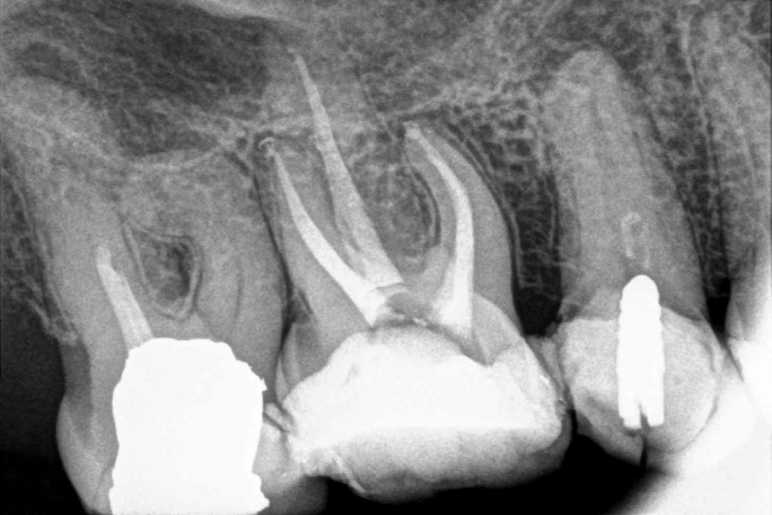
The maxillary molars are some of the most complex teeth in terms of anatomy, typically having three roots: two buccal (mesiobuccal and distobuccal) and one palatal. Each root generally contains one canal, although variations in canal anatomy are common. The mesiobuccal root, for instance, may have two canals in a significant number of cases (referred to as MB2 canals).
Due to the complexity of these molars, precise access opening is critical to locating all canals. Incomplete access can lead to missed canals, leading to failed root canal treatments and persistent infections.
Importance of Proper Access Opening
Before delving into the technique, it’s essential to understand why proper access opening in maxillary molars is so important:
- Complete Canal Access: Proper access ensures that all root canals, including the often hidden MB2 canal, are located and treated.
- Prevents Tooth Fracture: Incorrect access can weaken the tooth structure, leading to fractures during or after treatment.
- Efficient Pulp Removal: Adequate access allows for the complete removal of infected pulp tissue, which is crucial for successful endodontic treatment.
- Better Visualization: A well-prepared access cavity provides clear visibility of the chamber floor, making it easier to locate the canal orifices.
Step-by-Step Guide to Maxillary Molar Access Opening
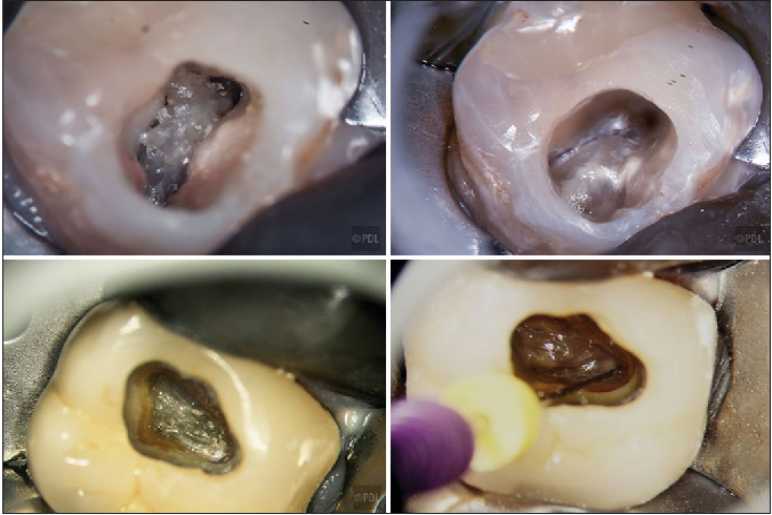
1. Preoperative Assessment
Before starting, it is essential to conduct a thorough assessment of the patient’s tooth using radiographs. Preoperative radiographs provide invaluable information about the tooth’s anatomy, including the size and shape of the pulp chamber, the curvature of the roots, and any abnormalities. Understanding the anatomy beforehand allows you to plan the access cavity more accurately.
2. Isolation
Proper isolation is necessary to ensure the success of the procedure. Use a rubber dam to isolate the tooth, which not only prevents contamination but also ensures patient comfort. A well-isolated tooth provides a clean working environment and improves visibility.
3. Initial Penetration
Begin the procedure with a high-speed handpiece using a round bur or fissure bur. Start at the central groove of the maxillary molar, typically near the mesial aspect, where the pulp chamber is most accessible. It’s important to penetrate through the enamel and into the dentin gradually.
Make sure to maintain a steady, controlled approach to avoid damage to the tooth structure.
4. Creating the Access Outline
Once the pulp chamber is penetrated, the next step is to enlarge the access cavity. The shape of the access opening should be triangular, with the base of the triangle towards the buccal side and the apex pointing palatally.
- Mesiobuccal and Distobuccal Canals: The buccal extension should give direct access to the mesiobuccal and distobuccal canals.
- Palatal Canal: Extend the access cavity palatally to allow for direct visualization and instrumentation of the palatal canal.
Be careful not to overextend, as this can weaken the remaining tooth structure.
5. Refining the Access Cavity
After initial access is created, use an endo-Z bur or similar non-cutting bur to refine the access cavity. The goal here is to smoothen the walls and floor of the cavity while avoiding gouging the chamber. A smooth and clean access cavity helps in locating the canal orifices more efficiently.
6. Locating the Canals
Once the pulp chamber is fully exposed, the next critical step is to locate the canal orifices. Using an endodontic explorer, gently feel around the chamber floor for canal openings. The pulpal floor typically exhibits color changes or depressions where the canals are located.
- Mesiobuccal Canal (MB1 and MB2): As mentioned earlier, the mesiobuccal root often has a second canal, MB2. This canal is often located mesial to or just behind the MB1 canal.
- Palatal and Distobuccal Canals: These are generally easier to locate due to their larger orifices.
7. Verification of Canal Access
After locating the canals, use small endodontic files to confirm that you have accessed the full canal system. Radiographs or cone-beam CT scans can help verify that all canals, including the elusive MB2 canal, have been identified and accessed.
8. Final Touches
Once all canals are located, the final step is to flare the coronal portion of each canal for easier instrumentation and irrigation. This process ensures efficient cleaning and shaping of the root canal system.
Tips for Successful Maxillary Molar Access Opening
- Stay Conservative: While it’s important to create an adequate access cavity, overzealous removal of tooth structure can compromise the tooth’s strength.
- Use Magnification: Dental loupes or microscopes can enhance visibility, especially when locating the MB2 canal.
- Constant Irrigation: Keep the chamber clean and free of debris by regularly irrigating during the procedure.
- Check for Variations: Be aware that maxillary molars have anatomical variations. Using radiographs or cone-beam CT imaging helps in visualizing these variations before accessing the tooth.
- Utilize Quality Instruments: High-quality endodontic tools play a pivotal role in ensuring successful access and treatment. AB Dentologic offers a range of premium dental instruments designed specifically for precision in endodontic procedures, including maxillary molar access opening. Their expertly crafted tools can aid dental professionals in achieving optimal results with minimal tooth damage.
Conclusion
Maxillary molar access opening is a delicate procedure requiring precision and a thorough understanding of dental anatomy. By following the right steps and using high-quality tools from reputable providers like AB Dentologic, dental professionals can perform more effective and efficient endodontic treatments. Mastering this technique not only improves patient outcomes but also enhances the practitioner’s skills and confidence in handling complex molar cases.
For more resources on endodontics and dental tools, explore the range of products offered by AB Dentologic. Their expertise and top-tier tools will elevate your dental practice to the next level.
Have A Look :-
